In-Depth Look at the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet


Intro
The Pediatric Glidescope Stylet has emerged as an indispensable tool in the sophisticated realm of pediatric airway management. As challenges arise in intubating children, especially those with unique anatomical considerations, understanding this device with its specific design, applications, and operational protocols is crucial. While the name may evoke images of technological advancement, it’s the practical application in real-world scenarios that truly highlights its value. This article aims to break down every element of the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet, paving the way for professionals and students alike to explore its impact on healthcare.
Research Overview
Summary of Key Findings
In recent research dedicated to pediatric intubation methods, several key insights have surfaced regarding the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet. One predominant finding emphasizes its well-rounded design, which incorporates advanced visualization technology to simplify the often tricky process of intubation in younger patients. By allowing for a clearer view of the airway, the device not only enhances procedural success rates but also minimizes complications post-intubation.
Furthermore, clinical trials indicate notable improvements in time efficiency when using the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet as opposed to conventional laryngoscopes. Many studies emphasize that this quicker intubation translates to better patient outcomes, especially in emergency scenarios.
Importance of the Research in Its Respective Field
The significance of this research cannot be understated. Intubation in pediatric cases frequently involves navigating unique anatomical challenges that can significantly impede standard practices. The Pediatric Glidescope Stylet addresses these challenges by providing healthcare practitioners with better tools and insights, ensuring that patient safety and comfort are at the forefront. It’s about more than just functionality; it’s about optimizing care when every second matters.
Methodology
Description of the Experimental or Analytical Methods Used
To gather data on the efficacy of the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet, a mixed-methods approach was adopted. Quantitative measures included controlled trials comparing cancellation rates and complication occurrences associated with intubation procedures. Moreover, qualitative interviews with anesthesiologists and pediatricians provided invaluable insight into the long-term impact of using this device in clinical practice.
Sampling Criteria and Data Collection Techniques
Participants in the study encompassed both practitioners with varied experience levels. This diversity ensured that findings were reflective of a broad spectrum of practice environments, from urban hospitals to smaller medical facilities. Data collection, on the other hand, utilized a combination of direct observation during procedures, along with structured surveys to capture the experiences and outcomes associated with the use of the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet.
"In a world where pediatric intubation can be fraught with risk, the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet stands out as a beacon of innovation, pushing the boundaries of what's possible in airway management."
By dissecting the nuances of the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet, this article strives to be a robust resource, peeling back the layers of research while shedding light on its clinical applications. As we navigate through various aspects, from the device's design to its role in contemporary medical practices, each section will enhance understanding of its vital place in pediatric healthcare.
Foreword to Pediatric Airway Management
In the realm of medicine, particularly in pediatrics, mastering airway management can be a pivotal juncture in ensuring patient safety and successful outcomes. Pediatric patients, due to their distinct anatomical features and physiological characteristics, require specialized approaches to airway management. These nuances make it essential for healthcare professionals to be well-versed in the intricacies of pediatric airway dynamics, which is fundamental to this article’s exploration of the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet.
Understanding Pediatric Airway Anatomy
The anatomy of a child’s airway is markedly different from that of an adult. One of the most notable distinctions lies in the proportion of the head and neck. In children, the head is relatively larger and the neck is shorter, which can complicate visualizing and accessing the airway. Moreover, the epiglottis in infants is more floppy and U-shaped, further complicating intubation. A grasp of these anatomical variations is crucial.
For instance, the narrowest part of a child's airway is at the cricoid ring rather than at the vocal cords, as is the case in adults. This information can be vital during emergencies, where speed and accuracy are crucial. Understanding these peculiarities equips medical staff with the knowledge to perform airway interventions more effectively.
Challenges in Pediatric Intubation
Intubating a child presents a unique set of hurdles. The small size of pediatric airways can make it difficult to secure adequate ventilation, especially under stress. Utilizing traditional methods and tools often does not yield the desired results, leading to increased complications. Some of the challenges faced include:
- Size Confusion: The disparity in equipment sizes can lead to inappropriate choices, which can be critical.
- Regurgitation: Pediatric patients often have more pronounced reflexes than adults, raising the risk of vomiting during intubation, creating further challenges.
- Anxiety in Patients: Younger patients may react unpredictably due to anxiety; thus, managing their comfort levels is of utmost importance.
Overcoming these challenges demands not only technical proficiency but also an intimate familiarity with the equipment and the variable nature of pediatric responses.
In summary, understanding the complexities underpinning pediatric airway management is foundational for professionals who seek effective and safe intubation methods. The Pediatric Glidescope Stylet emerges as a significant tool, offering insights into both operational protocols and the unique needs of this delicate patient demographic. Engaging with this material enables healthcare professionals to enhance both their practice and patient outcomes.
The Pediatric Glidescope Stylet: An Overview
In the realm of pediatric airway management, the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet stands out as a pivotal tool, one that demonstrates a sophisticated blend of engineering and clinical foresight. Its significance can't be overstated; this device addresses crucial challenges inherent in pediatric intubation, elevating both safety and efficacy in practice. Intuitively designed, it not only simplifies the complex process of intubation but also fosters confidence among practitioners navigating the intricacies of a child's airway.
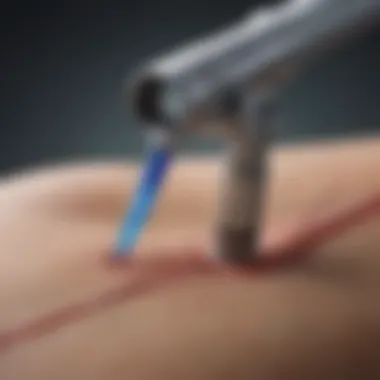

The Glidescope Stylet is crafted with specific design features that cater to the unique anatomical characteristics of pediatric patients. Often, traditional intubation techniques falter when faced with the smaller and less predictable airways of children. The Pediatric Glidescope Stylet, however, is tailored to meet those specific needs, thereby reducing the risks of complications that may arise from improper placement or unsuccessful attempts.
Design Features of the Glidescope Stylet
Diving deeper, the design features of the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet are nothing short of ingenious. The stylet boasts a lightweight frame, specifically shaped to accommodate a child's anatomy, promoting ease of access. Its flexibility allows for adjustments during the procedure, while maintaining a level of rigidity necessary for directional control. The integrated camera offers a view of the airway in real-time, significantly enhancing the visualization during intubation sessions.
Moreover, the tip of the stylet can be manipulated, which is essential as it allows for customization based on the individual child’s needs. The ergonomic design is not only aimed at usability but also minimizes fatigue for healthcare providers during prolonged procedures. By understanding the specific nuances of pediatric anatomy, designers have created a tool that feels almost intuitive, even in high-stress situations.
Technological Innovations
When discussing technological innovations, the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet sets a benchmark. The incorporation of advanced optical systems into the design is revolutionary. With high-definition imaging, practitioners can visualize the airway like never before, ensuring that they can identify complications instantly. This features aids in making real-time decisions that could be critical in emergency scenarios.
Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence is on the horizon, with potential applications in predicting complications based on previous intubation data. These technological advancements are not merely enhancements; they represent a future direction in the way pediatric intubation is approached.
"The introduction of the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet marks a transformative phase in pediatric airway management; it challenges conventional methods while offering pragmatic solutions to longstanding issues."
Operational Protocols for Use
The handling of the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet is far from a mere footnote in the broader discourse on pediatric airway management. Rather, understanding the operational protocols surrounding its use is vital for ensuring the safety and efficacy of intubation procedures. These protocols not only dictate the correct application of this innovative device but also enhance the overall clinical experience for both healthcare providers and pediatric patients.
When used correctly, the Glidescope Stylet can significantly reduce the intubation time, thus minimizing the stress and potential harm to a child under sedation. Following proper protocols ensures that the benefits of this technology are fully realized while also considering patient safety—a paramount concern.
Pre-Intubation Assessment
Before diving into the intubation process, assessing the child's condition is crucial. The pre-intubation assessment encompasses a thorough evaluation of the patient's airway, including any anatomical anomalies or unique features that might complicate the intubation. This can involve a visual inspection and, sometimes, diagnostic imaging if the circumstances allow.
The physician should consider:
- Age and Size of the Patient: Younger patients have distinct anatomical characteristics that differ notably from adults, which must be factored into the assessment.
- Medical History: Previous surgeries or conditions affecting the airway, such as tracheomalacia, can influence the intubation strategy.
- Current State: Acuteness of the situation may dictate whether speed or thoroughness takes precedence.
This assessment phase is critical, as it lays the groundwork for a successful intubation, guiding the choice of equipment and techniques down the line.
Step-by-Step Intubation Process
Once the pre-intubation assessment is completed, healthcare professionals can initiate the step-by-step intubation process with confidence. Using the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet, the following steps are generally adhered to:
- Preparation: Ensure that all necessary equipment, including the Glidescope and appropriate-sized endotracheal tubes, is readily available.
- Positioning: The child should be positioned appropriately, ideally supine with the neck slightly extended to optimize the airway view.
- Insertion of the Stylet: The Glidescope Stylet is inserted into the mouth and advanced carefully while visualizing the glottic opening on the attached monitor. This real-time imaging aids in navigating the challenging pediatric airway.
- Placement of Endotracheal Tube: Once the vocal cords are identified, the endotracheal tube can be thread through the Stylet into the trachea.
- Confirmation: After placement, it's vital to confirm correct tube placement by utilizing capnography and chest rise observation.
Each step should be carried out judiciously as this method significantly enhances visualization and overall intubation success rates in pediatric patients.
Post-Intubation Care
After the intubation process is achieved, the focus shifts to post-intubation management. This phase is often overlooked but is equally complex and significant in ensuring patient safety and effectiveness of airway maintenance.
Post-intubation care involves:
- Monitoring: Continuous evaluation of oxygen saturation, end-tidal CO2, and respiratory rate is essential to confirm ongoing adequate ventilation.
- Sedation Management: Maintaining appropriate sedation levels is crucial to avoid stress or discomfort for the patient.
- Tube Security: Ensure that the endotracheal tube is secured properly to prevent dislodgment during transport or patient movement.
- Plan for Extubation: Develop a strategy for extubation based on the child's status and surgical requirements.
"Effective post-intubation care not only protects the patient's airway but also reassures parents and caregivers about the child's wellbeing."
In summary, the operational protocols for using the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet emphasize careful consideration at every step. From the initial assessment through the intubation and to post-care, each phase is interconnected and essential for a successful outcome in pediatric airway management.
Clinical Applications and Benefits
In the realm of pediatric airway management, the utilization of the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet represents a significant leap forward in both technology and practical application. Understanding the various clinical contexts in which this device is employed helps underscore its pivotal role in enhancing both patient outcomes and procedural efficiencies. The Pediatric Glidescope Stylet is not just another tool; it embodies a collection of features that make it particularly suited for the nuances of pediatric intubation.


Use in Emergency Situations
Emergency intubations are often fraught with complications due to the unpredictable nature of the pediatric patient. The Pediatric Glidescope Stylet shines in this arena. The device is designed to assist clinicians in swiftly and accurately securing the airway in high-pressure scenarios, such as respiratory distress or trauma. Its intuitive design minimizes the need for extensive anatomical knowledge while providing an excellent visual field, which is critical when every second counts.
In instances of critical care, a quick yet effective response can determine outcomes. Observational data suggests that health professionals using the Stylet experience a reduction in intubation attempts, consequently lowering the risk of desaturation in children. The ergonomic features allow for enhanced maneuverability, making it easier to navigate the challenging anatomy of pediatric patients. Furthermore, the device can be used in cases of anatomic abnormalities, where traditional methods may falter.
"Speed and precision are the cornerstones of airway interventions in pediatrics. The Stylet enhances both, significantly improving the chances of success in emergencies."
Applications in Elective Procedures
While emergency contexts are a significant focus, the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet is equally valuable in elective procedures. Its integration into planned surgeries enables practitioners to anticipate challenges ahead of time. For instance, during elective surgeries such as tonsillectomies or adenoidectomies, where airway access is essential, the Stylet provides a reliable path through which intubation can be performed seamlessly.
Relying on the enhanced optics and design features, clinicians can maintain a balance of efficiency and safety, assuring parents and guardians of the well-being of their children. Moreover, using the Stylet in elective settings allows for an increased standardization of intubation practices across pediatric departments, aligning with best practices and enhancing overall procedural consistency.
Comparison with Traditional Methods
When juxtaposed with conventional intubation methods, the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet offers advantages that are hard to overlook. Traditional laryngoscopes may rely heavily on the operator's skill and familiarity with pediatric anatomy, which can vary widely among practitioners. In contrast, the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet introduces an element of technological support that bolsters skill levels, regardless of experience.
Some key differences include:
- Visualization: The angled blade design provides a better view of the vocal cords compared to conventional straight blades, which is especially useful in smaller airways.
- Success Rates: Studies indicate that the Stylet contributes to higher first-pass success rates, meaning less trauma and stress for the child.
- User-Friendliness: It requires less force and manipulation, therefore reducing the chances of airway trauma, which can be particularly concerning in pediatric cases.
Safety Considerations
In pediatric airway management, safety is not just a checkbox; it’s the bedrock upon which procedures are built. Parents trust healthcare professionals with their children’s lives, underscoring the critical importance of a meticulous approach to intubation practices. The Pediatric Glidescope Stylet emerges as a beacon in this domain, facilitating not just ease of use but also enhancing patient safety. A thorough understanding of safety considerations when using the stylet can not only streamline the intubation process but also minimize complications and promote better outcomes.
Complications Associated with Intubation
Intubation, though often necessary, carries a risk of various complications. The more you know about these potential issues, the better you can prepare to handle them. Complications can range from minor incidents to catastrophic events. Some of the most prevalent complications include:
- Esophageal Intubation: When the tube is placed in the esophagus instead of the trachea, leading to inadequate ventilation.
- Trauma to Airway Structures: This can include damage to the vocal cords or other delicate structures.
- Barotrauma: This is caused by excessive pressure during ventilation, potentially leading to lung injury.
- Hypoxia: If intubation takes longer than expected or is unsuccessful, the child may suffer a lack of oxygen.
- Pulmonary Aspiration: Inhalation of foreign material into the lungs, which can lead to severe complications.
Recognizing these risks is vital not only for planning but also for adapting techniques during the procedure. It helps practitioners anticipate complications, ensuring parents are appropriately informed and reassured throughout the process.
Minimizing Risks with the Stylet
The Pediatric Glidescope Stylet is not just another tool in the kit; it's engineered with safety in mind, which can significantly mitigate known intubation risks. By augmenting visualization and facilitating better control over the intubation, the stylet offers several advantages:
- Enhanced Visualization: The LED display provides a clear view of airway anatomy, making it easier to avoid common pitfalls.
- Flexible Design: Its curvature and consistency help navigate challenging airways efficiently, reducing the chances of trauma.
- Real-Time Feedback: The integration of technology allows for immediate visualization, providing greater assurance that the tube is placed in the correct position.
"Effective intervention in pediatric intubation not only hinges on skill but also on the tools utilized. The Glidescope Stylet can be a game changer in fostering both precision and safety."
- Adaptability: With its design, practitioners can adjust techniques mid-procedure, increasing success rates in real-time.
- Training Tools: The stylet serves as an educational aid, helping to familiarize new practitioners with proper techniques in a controlled environment.
By understanding these features and the corresponding safety mechanisms, healthcare professionals can vastly improve the likelihood of successful intubation while minimizing risks associated with traditional methods. In a field where every second counts, leveraging advancements in technology like the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet can make the world of difference.
Case Studies and Research Insights
In the ever-evolving field of pediatric intubation, case studies and research insights serve as the backbone for understanding the practical applications of the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet. They illuminate the real-world impact of this technology on patient outcomes and provide healthcare professionals with evidence-based guidance for its use in diverse clinical scenarios. By analyzing successful intubation cases and comparative studies across pediatric populations, practitioners can enhance their skills and reduce the inherent risks associated with airway management in children.
Successful Intubations Using the Stylet
Successful intubations using the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet illustrate the device's effectiveness in complex situations. There’s no shortage of real-life instances that highlight its superiority in certain contexts, particularly in cases where traditional methods have faltered. For example, a recent case at a major children's hospital documented the successful intubation of a four-year-old with an obstructive airway anomaly. Using the Glidescope Stylet, the team facilitated a smooth intubation, achieving good ventilation while avoiding trauma to the delicate anatomical structures.


- Benefits revealed from these cases include:
- Improved Visualization: Enhanced camera angles provide a clearer view of the airway.
- Reduced Intubation Times: Faster procedures lead to decreased stress for the patient and healthcare team.
- Lower Complication Rates: Reductions in complications such as teeth damage or esophageal intubation have been reported.
"The Pediatric Glidescope Stylet has transformed how we approach pediatric intubation, turning what used to be a daunting task into a more manageable procedure," reflect seasoned anesthetists working in pediatric emergency settings.
Comparative Studies in Pediatric Populations
Comparative studies that measure the outcomes of intubation methods offer a rich source of insights into the effectiveness of the Glidescope Stylet versus traditional alternatives. One notable study encompassed a cohort of 120 children undergoing elective and emergency surgeries, comparing the Glidescope with conventional rigid laryngoscopes.
The results were telling:
- First Pass Success Rate: The Glidescope Stylet demonstrated a first-pass success rate of 84%, significantly higher than the 67% achieved with standard methods.
- Anesthesia Duration: There was a notable reduction in overall anesthesia duration in cases employing the Glidescope, which contributed to quicker recovery times for patients.
- Patient Satisfaction: Parents reported lower anxiety levels when informed about the use of modern technology for their child's procedure, indicating a visible convergence between technology and improved wider patient experiences.
The ongoing research solidifies the position of the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet as a valuable tool, not merely anecdotal but underpinned by empirical evidence that encourages its integration into routine practice. As pediatric health care continues to advance, leaning into robust studies will guide practitioners in making informed decisions for the benefit of their young patients.
Future Directions in Pediatric Intubation Technology
The landscape of pediatric intubation is evolving, driven by technological advancements that promise not only to improve the efficacy of procedures but also to enhance the safety of our most vulnerable patients. Understanding future directions in this field is crucial, especially when taking into account the complex dynamics often at play during pediatric airway management. As technology progresses, there is a growing emphasis on integrating innovative designs and artificial intelligence to expand the capabilities of devices like the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet.
Potential Innovations in Stylet Design
The design of intubation devices is critical to their functionality. Modern stylets are being reimagined to facilitate easier handling and improved navigation of pediatric airways. Potential innovations include:
- Flexible Materials: Development of stylets from new flexible materials could allow for better adaptability to the anatomical variations seen in pediatric patients.
- Ergonomic Handles: Incorporating ergonomically designed handles could significantly enhance the user experience, promoting better grip and precision when maneuvering the device.
- Modular Components: Future designs may include modular aspects that permit customization based on the specific needs of the patient or the intubation situation, such as different lengths or curve shapes.
These innovations not only enhance device efficacy but also prioritize patient comfort and safety, addressing the unique challenges posed by intubating children.
Integration of AI in Intubation Procedures
Artificial intelligence (AI) stands on the cusp of transforming pediatric intubation procedures. By harnessing AI, clinicians could access valuable support that augments their skill sets. Potential integration avenues include:
- Real-Time Data Analysis: AI could facilitate the analysis of large sets of clinical data during intubation, providing real-time feedback to guide clinicians through the procedure.
- Predictive Algorithms: Algorithms could be developed to predict difficulties in intubation scenarios based on patient history or presentation, helping clinicians prepare better.
- Simulation and Training Tools: AI-driven simulators could offer healthcare providers realistic training environments, refining their intubation techniques without putting patients at risk.
By embracing such technologies, practitioners can better navigate the intricacies involved with pediatric intubation, ultimately leading to more successful outcomes.
"Technological evolution in the medical field is not just about effectiveness; it's about redefining standards in patient care. The future certainly looks promising in the realm of pediatric airway management."
As the field advances, the incorporation of cutting-edge technologies like enhanced stylet designs and AI-driven protocols will constitute a baseline for improving healthcare delivery. These advancements reflect a broader commitment to enhancing both efficacy and safety in pediatric intubation.
Epilogue and Implications for Practice
The exploration of the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet brings to light its vital role in enhancing pediatric airway management. When discussing the conclusion and the implications for practice, it is crucial to synthesize the information presented throughout the article. The Glidescope Stylet offers distinct advantages in terms of design and functionality which directly contribute to better clinical outcomes in pediatric intubation.
The importance of selecting the right tools for intubation practices cannot be overstated. Proper equipment, such as the Glidescope Stylet, reduces complications, enhances the visualization of the airway, and ultimately contributes to safer intubation experiences. Medical professionals must be familiar with how to effectively integrate this device into their workflow—this includes knowledge about its operation, procedural protocols, and the specific population it serves. A deeper understanding of these factors undoubtedly aids in optimal patient care, particularly in emergency scenarios where rapid decisions are needed.
Considerations about continuing education and skill maintenance cannot be overlooked. As technology evolves, healthcare professionals must stay abreast of innovations in devices like the Glidescope Stylet to safeguard against complacency in their practice. Regular training sessions should focus on simulation experiences where the use of the stylet is practiced in various clinical situations. This will solidify its place as an essential tool in a medical team's arsenal.
"Choosing the right tools can mean the difference between success and failure in pediatric airway management."
Like any medical device, ongoing research and evaluations of the Glidescope Stylet will further validate its role in practice, leading to refinements that will improve patient safety. As the body of evidence grows, practitioners should advocate for continued inclusion of such devices in their clinical practice.
Summary of Key Points
- The Pediatric Glidescope Stylet significantly improves visualization during intubation, reducing the risks associated with pediatric airway management.
- Proper selection and familiarization with the device can enhance patient outcomes and is crucial in emergency scenarios.
- Continuous education and training are vital for effective use, ensuring healthcare professionals can leverage the latest advancements in technology.
- Ongoing research will help validate and improve the use of the Glidescope Stylet in various healthcare settings, keeping it at the forefront of pediatric intubation tools.
Recommendations for Healthcare Professionals
- Engage in Regular Training: Take part in workshops and simulation exercises that focus specifically on the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet. Familiarity with the device can make a significant difference in high-pressure situations.
- Incorporate Evidence-Based Practices: Stay updated with the latest research findings and review case studies that highlight the successful use of the Glidescope Stylet.
- Build Interprofessional Collaborations: Discuss experiences and techniques within multidisciplinary teams to share insights and improve practices across different specialties.
- Advocate for Continued Learning: Promote a culture in your institution where continuous education regarding new devices and methodologies is encouraged and supported.
- Monitor and Evaluate Outcomes: Establish a protocol for reviewing intubation outcomes with the Glidescope Stylet to identify areas for improvement and address any complications that arise, thereby refining the overall process.
Advocating for the use of innovative tools like the Pediatric Glidescope Stylet can elevate pediatric intubation practices. By keeping abreast of the technology and actively engaging in continuous education, healthcare professionals can ensure best practices in airway management for pediatric patients.







